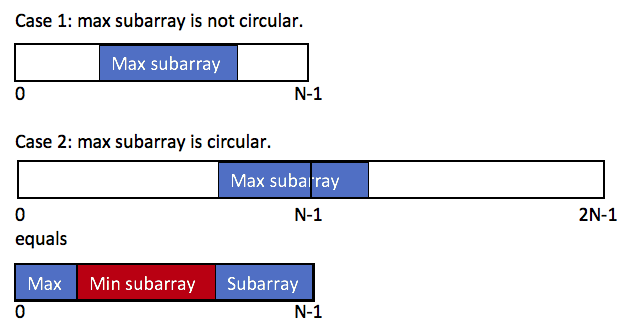
Maximum Sum Circular Subarray
Given a circular array C of integers represented by A, find the maximum possible sum of a non-empty subarray of C.
Here, a circular array means the end of the array connects to the beginning of the array. (Formally, C[i] = A[i] when 0 <= i < A.length, and C[i+A.length] = C[i] when i >= 0.)
Also, a subarray may only include each element of the fixed buffer A at most once. (Formally, for a subarray C[i], C[i+1], ..., C[j], there does not exist i <= k1, k2 <= j with k1 % A.length = k2 % A.length.)
Example 1:
Input: [1,-2,3,-2] Output: 3 Explanation: Subarray [3] has maximum sum 3
Example 2:
Input: [5,-3,5] Output: 10 Explanation: Subarray [5,5] has maximum sum 5 + 5 = 10
Example 3:
Input: [3,-1,2,-1] Output: 4 Explanation: Subarray [2,-1,3] has maximum sum 2 + (-1) + 3 = 4
Example 4:
Input: [3,-2,2,-3] Output: 3 Explanation: Subarray [3] and [3,-2,2] both have maximum sum 3
Example 5:
Input: [-2,-3,-1] Output: -1 Explanation: Subarray [-1] has maximum sum -1
Note:
- -30000 <= A[i] <= 30000
- 1 <= A.length <= 30000
class Solution {
public int maxSubarraySumCircular(int[] A) {
int maxSubSum = A[0], minSubSum = A[0], currMax = A[0], currMin = A[0], total = A[0];
for (int i = 1; i < A.length; i ++) {
currMax = Math.max(currMax + A[i], A[i]);
maxSubSum = Math.max(currMax, maxSubSum);
currMin = Math.min(currMin + A[i], A[i]);
minSubSum = Math.min(currMin, minSubSum);
total += A[i];
}
return maxSubSum > 0 ? Math.max(maxSubSum, total - minSubSum) : maxSubSum;
}
}