Gray Code
The gray code is a binary numeral system where two successive values differ in only one bit.
Given a non-negative integer n representing the total number of bits in the code, print the sequence of gray code. A gray code sequence must begin with 0.
For example, given n = 2, return [0,1,3,2]. Its gray code sequence is:
00 - 0 01 - 1 11 - 3 10 - 2
There might be multiple gray code sequences possible for a given n.
Return any such sequence.
Method 1:
Use a set to keep track of existed number
Solution 1:
Time: O(n^n)
Space: O(2^n)
public class Solution {
public ArrayList<Integer> grayCode(int a) {
List<Integer> list = new ArrayList<>();
for (int i = 0; i < a; i ++) {
list.add(0);
}
ArrayList<Integer> result = new ArrayList<>();
Set<Integer> set = new HashSet<>();
result.add(0);
set.add(0);
helper(result, list, set);
return result;
}
private void helper(ArrayList<Integer> result, List<Integer> list, Set<Integer> set) {
if (result.size() == (int) Math.pow(2, list.size())) {
return;
}
for (int i = 0; i < list.size(); i ++) {
int val = 1 - list.get(i);
list.set(i, val);
int decimal = toDecimal(list);
if (set.add(decimal)) {
result.add(decimal);
helper(result, list, set);
break;
}
list.set(i, 1 - val);
}
}
private int toDecimal(List<Integer> list) {
int decimal = 0;
for (int i = list.size() - 1; i >= 0; i --) {
int power = list.size() - 1 - i;
decimal += (int) Math.pow(2, power) * list.get(i);
}
return decimal;
}
}
Method 2:
n位元的格雷码可以从n-1位元的格雷码以上下镜射后加上新位元的方式快速的得到,如下图所示一般。
Return any such sequence.
Method 1:
Use a set to keep track of existed number
Solution 1:
Time: O(n^n)
Space: O(2^n)
public class Solution {
public ArrayList<Integer> grayCode(int a) {
List<Integer> list = new ArrayList<>();
for (int i = 0; i < a; i ++) {
list.add(0);
}
ArrayList<Integer> result = new ArrayList<>();
Set<Integer> set = new HashSet<>();
result.add(0);
set.add(0);
helper(result, list, set);
return result;
}
private void helper(ArrayList<Integer> result, List<Integer> list, Set<Integer> set) {
if (result.size() == (int) Math.pow(2, list.size())) {
return;
}
for (int i = 0; i < list.size(); i ++) {
int val = 1 - list.get(i);
list.set(i, val);
int decimal = toDecimal(list);
if (set.add(decimal)) {
result.add(decimal);
helper(result, list, set);
break;
}
list.set(i, 1 - val);
}
}
private int toDecimal(List<Integer> list) {
int decimal = 0;
for (int i = list.size() - 1; i >= 0; i --) {
int power = list.size() - 1 - i;
decimal += (int) Math.pow(2, power) * list.get(i);
}
return decimal;
}
}
Method 2:
n位元的格雷码可以从n-1位元的格雷码以上下镜射后加上新位元的方式快速的得到,如下图所示一般。
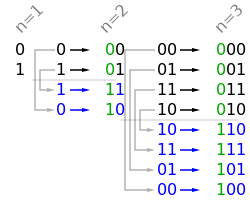
Solution:
Time: O(2^n)
Space: O(2^n)
public class Solution {
public ArrayList<Integer> grayCode(int a) {
ArrayList<Integer> result = new ArrayList<>();
result.add(0);
for (int i = 0; i < a; i ++) {
int size = result.size();
for (int j = size - 1; j >= 0; j --) {
result.add((1 << i) | result.get(j));
}
}
return result;
}
}