Rank Transform of a Matrix
Given an m x n matrix, return a new matrix answer where answer[row][col] is the rank of matrix[row][col].
The rank is an integer that represents how large an element is compared to other elements. It is calculated using the following rules:
- If an element is the smallest element in its row and column, then its rank is 1.
- If two elements p and q are in the same row or column, then:
- If p < q then rank(p) < rank(q)
- If p == q then rank(p) == rank(q)
- If p > q then rank(p) > rank(q)
- The rank should be as small as possible.
It is guaranteed that answer is unique under the given rules.
Example 1:
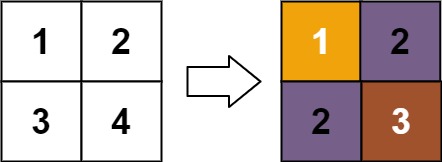
Input: matrix = [[1,2],[3,4]] Output: [[1,2],[2,3]] Explanation: The rank of matrix[0][0] is 1 because it is the smallest integer in its row and column. The rank of matrix[0][1] is 2 because matrix[0][1] > matrix[0][0] and matrix[0][0] is rank 1. The rank of matrix[1][0] is 2 because matrix[1][0] > matrix[0][0] and matrix[0][0] is rank 1. The rank of matrix[1][1] is 3 because matrix[1][1] > matrix[0][1], matrix[1][1] > matrix[1][0], and both matrix[0][1] and matrix[1][0] are rank 2.
Example 2:
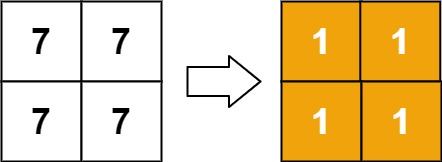
Input: matrix = [[7,7],[7,7]] Output: [[1,1],[1,1]]
Example 3:
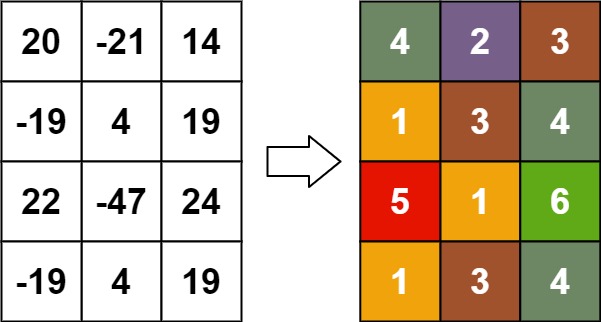
Input: matrix = [[20,-21,14],[-19,4,19],[22,-47,24],[-19,4,19]] Output: [[4,2,3],[1,3,4],[5,1,6],[1,3,4]]
Example 4:
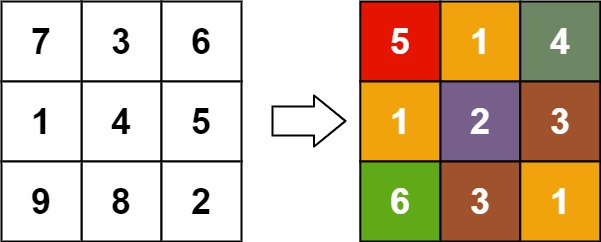
Input: matrix = [[7,3,6],[1,4,5],[9,8,2]] Output: [[5,1,4],[1,2,3],[6,3,1]]
Constraints:
- m == matrix.length
- n == matrix[i].length
- 1 <= m, n <= 500
- -109 <= matrix[row][col] <= 109
Solution:
class Solution {
public int[][] matrixRankTransform(int[][] matrix) {
int m = matrix.length, n = matrix[0].length;
int[] rank = new int[m + n];
TreeMap<Integer, List<int[]>> d = new TreeMap();
for (int i = 0; i < m; i ++) {
for (int j = 0; j < n; j ++) {
d.putIfAbsent(matrix[i][j], new ArrayList());
d.get(matrix[i][j]).add(new int[]{i, j});
}
}
int[] initP = new int[m + n];
for (int i = 0; i < initP.length; i ++) {
initP[i] = i;
}
for (int val : d.keySet()) {
int[] p = initP.clone();
int[] rank2 = rank.clone();
for (int[] cord : d.get(val)) {
int i = cord[0], j = cord[1];
int rootI = find(p, i), rootJ = find(p, j + m);
p[rootI] = rootJ;
rank2[rootJ] = Math.max(rank2[rootI], rank2[rootJ]);
}
for (int[] cord : d.get(val)) {
int i = cord[0], j = cord[1];
rank[i] = rank[j + m] = matrix[i][j] = rank2[find(p, i)] + 1;
}
}
return matrix;
}
private int find(int[] p, int x) {
while (p[x] != x) {
p[x] = p[p[x]];
x = p[x];
}
return x;
}
}