Minimum Time to Collect All Apples in a Tree
Given an undirected tree consisting of n vertices numbered from 0 to n-1, which has some apples in their vertices. You spend 1 second to walk over one edge of the tree. Return the minimum time in seconds you have to spend in order to collect all apples in the tree starting at vertex 0 and coming back to this vertex.
The edges of the undirected tree are given in the array edges, where edges[i] = [fromi, toi] means that exists an edge connecting the vertices fromi and toi. Additionally, there is a boolean array hasApple, where hasApple[i] = true means that vertex i has an apple, otherwise, it does not have any apple.
Example 1:
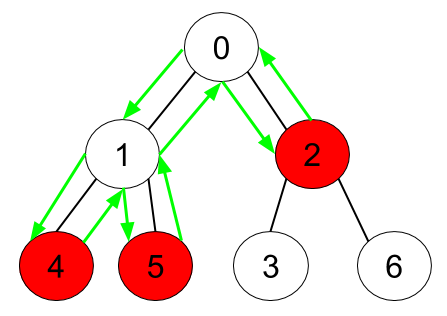
Input: n = 7, edges = [[0,1],[0,2],[1,4],[1,5],[2,3],[2,6]], hasApple = [false,false,true,false,true,true,false] Output: 8 Explanation: The figure above represents the given tree where red vertices have an apple. One optimal path to collect all apples is shown by the green arrows.
Example 2:
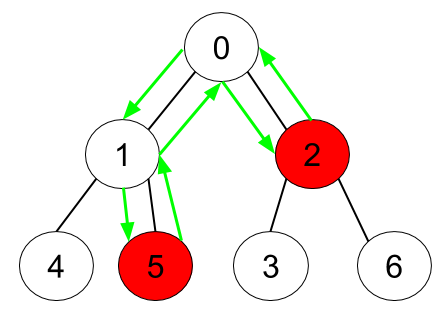
Input: n = 7, edges = [[0,1],[0,2],[1,4],[1,5],[2,3],[2,6]], hasApple = [false,false,true,false,false,true,false] Output: 6 Explanation: The figure above represents the given tree where red vertices have an apple. One optimal path to collect all apples is shown by the green arrows.
Example 3:
Input: n = 7, edges = [[0,1],[0,2],[1,4],[1,5],[2,3],[2,6]], hasApple = [false,false,false,false,false,false,false] Output: 0
Constraints:
- 1 <= n <= 10^5
- edges.length == n-1
- edges[i].length == 2
- 0 <= fromi, toi <= n-1
- fromi < toi
- hasApple.length == n
Solution:
class Solution {
public int minTime(int n, int[][] edges, List<Boolean> hasApple) {
Set<Integer> onstack = new HashSet();
Map<Integer, Set<Integer>> graph = new HashMap();
for (int[] edge : edges) {
int a = edge[0];
int b = edge[1];
Set<Integer> aNei = graph.getOrDefault(a, new HashSet());
Set<Integer> bNei = graph.getOrDefault(b, new HashSet());
if (onstack.contains(b)) {
bNei.add(a);
graph.put(b, bNei);
} else {
aNei.add(b);
graph.put(a, aNei);
}
onstack.add(a);
onstack.add(b);
}
int res = dfs(0, graph, hasApple);
return res > 0 ? res - 2 : 0;
}
private int dfs(int curr, Map<Integer, Set<Integer>> graph, List<Boolean> hasApple) {
int res = 0;
for (int child : graph.getOrDefault(curr, new HashSet<Integer>())) {
res += dfs(child, graph, hasApple);
}
// System.out.println(curr + ", " + res);
if (res > 0) {
return 2 + res;
} else if (hasApple.get(curr)) {
return 2;
} else {
return 0;
}
}
}