Number of Good Leaf Nodes Pairs
Given the root of a binary tree and an integer distance. A pair of two different leaf nodes of a binary tree is said to be good if the length of the shortest path between them is less than or equal to distance.
Return the number of good leaf node pairs in the tree.
Example 1:
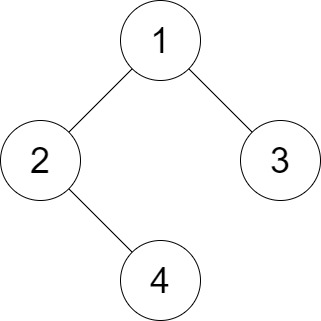
Input: root = [1,2,3,null,4], distance = 3 Output: 1 Explanation: The leaf nodes of the tree are 3 and 4 and the length of the shortest path between them is 3. This is the only good pair.
Example 2:
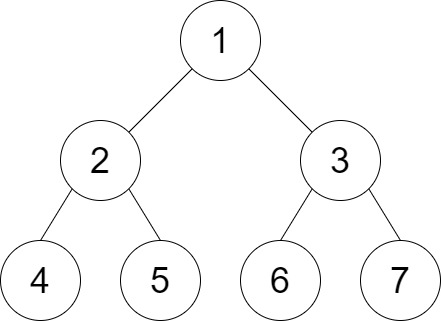
Input: root = [1,2,3,4,5,6,7], distance = 3 Output: 2 Explanation: The good pairs are [4,5] and [6,7] with shortest path = 2. The pair [4,6] is not good because the length of ther shortest path between them is 4.
Example 3:
Input: root = [7,1,4,6,null,5,3,null,null,null,null,null,2], distance = 3 Output: 1 Explanation: The only good pair is [2,5].
Example 4:
Input: root = [100], distance = 1 Output: 0
Example 5:
Input: root = [1,1,1], distance = 2 Output: 1
Constraints:
- The number of nodes in the tree is in the range [1, 2^10].
- Each node's value is between [1, 100].
- 1 <= distance <= 10
Solution:
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode() {}
* TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) {
* this.val = val;
* this.left = left;
* this.right = right;
* }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public int countPairs(TreeNode root, int distance) {
if (root == null) {
return 0;
}
int[] count = new int[1];
Map<Integer, Integer> map = helper(root, distance, count);
return count[0];
}
private Map<Integer, Integer> helper(TreeNode root, int distance, int[] count) {
// { distance: count }
Map<Integer, Integer> map = new HashMap();
if (root == null) return map;
if (root.left == null && root.right == null) {
map.put(1, 1);
return map;
}
Map<Integer, Integer> left = helper(root.left, distance, count);
Map<Integer, Integer> right = helper(root.right, distance, count);
if (left.size() > 0 && right.size() > 0) {
List<Integer> lkeys = new ArrayList<>(left.keySet());
List<Integer> rkeys = new ArrayList<>(right.keySet());
for (int i = 0; i < lkeys.size(); i ++) {
for (int j = 0; j < rkeys.size(); j ++) {
if (lkeys.get(i) + rkeys.get(j) <= distance) {
count[0] += left.get(lkeys.get(i)) * right.get(rkeys.get(j));
}
}
}
}
for (Map.Entry<Integer, Integer> entry : left.entrySet()) {
int newCount = entry.getKey() + 1;
map.put(newCount, map.getOrDefault(newCount, 0) + entry.getValue());
}
for (Map.Entry<Integer, Integer> entry : right.entrySet()) {
int newCount = entry.getKey() + 1;
map.put(newCount, map.getOrDefault(newCount, 0) + entry.getValue());
}
return map;
}
}