Vertical Order Traversal of a Binary Tree
Given a binary tree, return the vertical order traversal of its nodes values.
For each node at position (X, Y), its left and right children respectively will be at positions (X-1, Y-1) and (X+1, Y-1).
Running a vertical line from X = -infinity to X = +infinity, whenever the vertical line touches some nodes, we report the values of the nodes in order from top to bottom (decreasing Y coordinates).
If two nodes have the same position, then the value of the node that is reported first is the value that is smaller.
Return an list of non-empty reports in order of X coordinate. Every report will have a list of values of nodes.
Example 1:
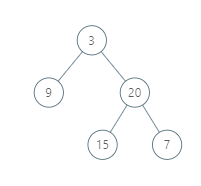
Input: [3,9,20,null,null,15,7] Output: [[9],[3,15],[20],[7]] Explanation: Without loss of generality, we can assume the root node is at position (0, 0): Then, the node with value 9 occurs at position (-1, -1); The nodes with values 3 and 15 occur at positions (0, 0) and (0, -2); The node with value 20 occurs at position (1, -1); The node with value 7 occurs at position (2, -2).
Example 2:
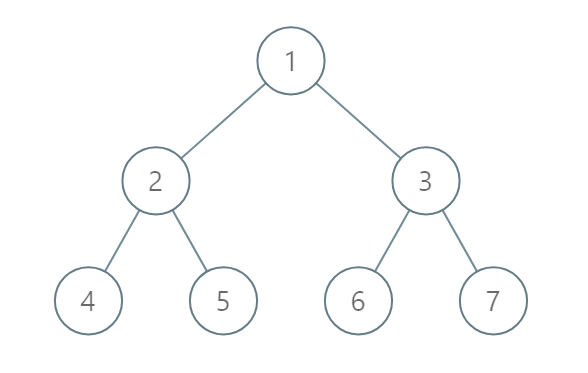
Input: [1,2,3,4,5,6,7] Output: [[4],[2],[1,5,6],[3],[7]] Explanation: The node with value 5 and the node with value 6 have the same position according to the given scheme. However, in the report "[1,5,6]", the node value of 5 comes first since 5 is smaller than 6.
Note:
- The tree will have between 1 and 1000 nodes.
- Each node's value will be between 0 and 1000.
Solution:
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode() {}
* TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) {
* this.val = val;
* this.left = left;
* this.right = right;
* }
* }
*/
class Solution {
class Node implements Comparable<Node> {
int d;
int v;
public Node(int d, int v) {
this.d = d;
this.v = v;
}
@Override
public int compareTo(Node n) {
if (Integer.compare(d, n.d) == 0) {
return Integer.compare(v, n.v);
}
return Integer.compare(d, n.d);
}
}
public List<List<Integer>> verticalTraversal(TreeNode root) {
Map<Integer, PriorityQueue<Node>> map = new HashMap();
pre(root, map, 0, 0);
List<List<Integer>> result = new ArrayList();
for (int p = -500; p <= 500; p ++) {
if (map.containsKey(p)) {
PriorityQueue<Node> nodes = map.get(p);
List<Integer> curr = new ArrayList();
while (!nodes.isEmpty()) {
curr.add(nodes.poll().v);
}
result.add(curr);
}
}
return result;
}
private void pre(TreeNode root, Map<Integer, PriorityQueue<Node>> map, int p, int d) {
map.putIfAbsent(p, new PriorityQueue());
map.get(p).add(new Node(d, root.val));
if (root.left != null) {
pre(root.left, map, p - 1, d + 1);
}
if (root.right != null) {
pre(root.right, map, p + 1, d + 1);
}
}
}/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode() {}
* TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) {
* this.val = val;
* this.left = left;
* this.right = right;
* }
* }
*/
class Solution {
Map<Integer, PriorityQueue<int[]>> map = new TreeMap();
public List<List<Integer>> verticalTraversal(TreeNode root) {
pre(root, 0, 0);
List<List<Integer>> result = new ArrayList();
for (int h : map.keySet()) {
List<Integer> list = new ArrayList();
while (!map.get(h).isEmpty()) {
list.add(map.get(h).poll()[1]);
}
result.add(list);
}
return result;
}
private void pre(TreeNode root, int d, int h) {
if (root == null) return;
// [d, val]
map.putIfAbsent(h, new PriorityQueue<int[]>((a, b) -> a[0] - b[0] == 0 ? a[1] - b[1] : a[0] - b[0]));
map.get(h).offer(new int[]{d, root.val});
pre(root.left, d + 1, h - 1);
pre(root.right, d + 1, h + 1);
}
}